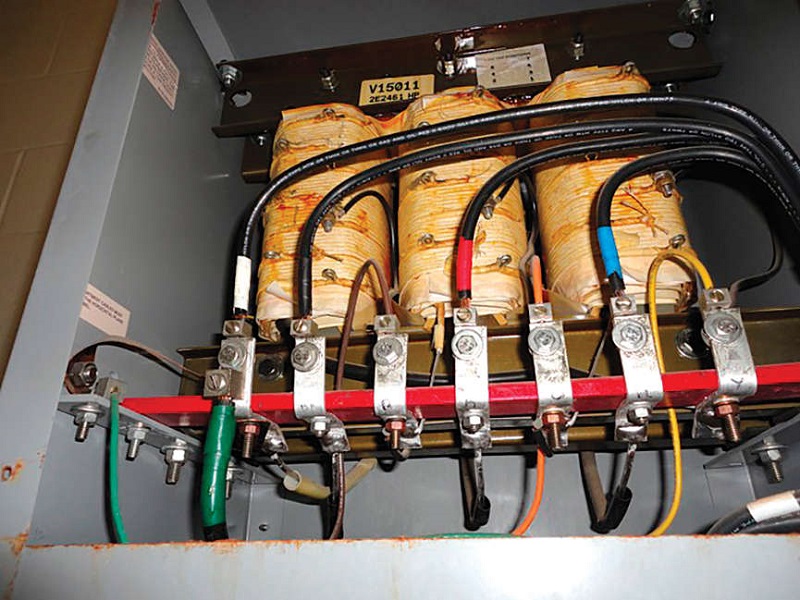
When it comes to the world of electrical work, terminology can sometimes be confusing and easily misunderstood. It’s essential for both electricians and their clients to have a solid grasp of the various devices used in electrical systems, particularly those crucial for safety purposes.
One such device is often referred to as a “disconnect,” which plays a vital role in preventing accidents and ensuring the proper functioning of equipment. So what exactly are these disconnects that electricians use? In this blog post, we’ll delve into the importance of understanding different types of disconnects, how they function within an electrical system, and why proper installation and maintenance are essential.
Understanding Disconnecting Means In Electrical Terminology
Disconnecting Means are essential components of any electrical system as they provide a safe and easy way to isolate the power source from the connected devices or equipment, allowing service personnel to work on them without fear of electrocution.
Definition And Function Of Disconnecting Means
Disconnecting means to play a crucial role in electrical systems, as they allow for the safe and efficient interruption of power flow within circuits. Essentially, disconnects ensure that electricians can safely perform maintenance or repairs on electrical equipment by cutting off the supply of electricity from a primary source.
For example, consider an industrial setting with heavy machinery powered through various circuits and wiring systems. An electrician may need to make adjustments or troubleshoot issues within these machines; without proper disconnecting means in place, this task becomes both challenging and dangerous.
Types Of Disconnecting Means
Disconnecting means come in different types, and it is important to understand these types to ensure proper installation and maintenance. Here are some of the common types:
- Fusible Disconnects: These disconnects contain fuses that blow when there is an overload or short circuit. This helps protect the equipment and prevent damage.
- Non-Fusible Disconnects: Unlike fusible disconnects, non-fusible disconnects do not have fuses. They simply break the connection between the power source and the device.
- Motor Disconnects: These are used specifically for motors and provide a way to safely turn them off when needed. They may have additional features like overload protection.
- Circuit Breaker Disconnects: These are commonly used in residential and commercial applications to protect circuits from overloads or short circuits.
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) Disconnects: These are designed to protect against electrocution by interrupting power in case of a ground fault.
- Service Entrance Disconnects: These disconnects are installed at the utility service entrance and are used by utility companies to shut off power during maintenance or emergencies.
Understanding these different types of disconnecting means can help electricians choose the appropriate one for each application, ensuring both safety and functionality.
When Disconnecting Means Are Required
Disconnecting means are required in numerous electrical applications to ensure safety and prevent hazards from occurring. For instance, whenever an electrician is working on any electrical equipment or device, they must disconnect the power source by using a suitable disconnecting means.
There are various scenarios that require the use of Disconnecting Means, such as servicing a fixture or motor, replacing fuses or breakers, and carrying out maintenance work on conductors.
Additionally, they are mandatory in cases where machines need repairs or adjustments while still powered on.
The Confusion Of Switches And Disconnects For Electricians
Electricians may sometimes be confused by the interchangeability of terminology between switches and disconnects, leading to misunderstandings when discussing different types of electrical devices used for controlling power sources.
Interchangeability Of Terminology
Electricians often have to deal with interchangeable terms when it comes to switches and disconnects, which can sometimes cause confusion. For instance, a switch may be referred to as a disconnect or vice versa, depending on the specific context.
For example, in some areas, an air conditioning unit’s main power shut-off device is called a contactor, while others refer to it as a disconnect switch. This interchangeability of terminology highlights the need for communication and clarity among electricians working together on any particular project.
Ultimately, regardless of what they are called, both switches and disconnects play critical roles in ensuring electrical safety and the proper functioning of equipment.
Commonly Used Terminology
In the world of electrical work, there are several commonly used terms that refer to disconnects and switches. Some of these terms include power disconnects, circuit breakers, and motor disconnects.
Power disconnects are used to shut off power from a source or group of devices and can be either fused or non-fused. Circuit breakers protect against overloads and short circuits in a circuit by automatically tripping open when an overload is detected.
It’s essential for electricians to understand and properly use these terms as they communicate with their team members about installing fixtures or working on machines that involve various electrical connections such as distribution boards, electrical service entrances, grounding systems, etc. By using the correct terminology associated with switches and disconnecting means, electricians can ensure all involved parties have a clear understanding of what needs to be done during installation or maintenance tasks while minimizing safety hazards related to ungrounded conductors or machine guards.
The Importance Of Proper Disconnecting Means In Electrical Work
Proper disconnecting means are crucial in electrical work to ensure safety and reduce liability issues.
Safety Concerns
Safety concerns are paramount when it comes to electrical work, especially regarding proper disconnecting means. Different types of disconnects and their installation should be done carefully to avoid potential hazards such as electrocution or fire.
These safety issues can lead to serious liability for contractors if not properly addressed. Electrical service entrances, distribution boards, machine guards, and other electrical components must meet certain standards to protect everyone involved from harm.
This is why identifying different types of disconnects and ensuring proper installation and maintenance are essential practices in the industry.
Liability Issues
Proper installation and maintenance of disconnecting means are crucial not only for safety reasons but also to avoid potential liability issues. In cases where an electrician fails to install the correct type of disconnecting means or improperly installs one, it can result in serious harm to individuals and property damage.
For example, suppose an electrician does not properly identify the appropriate type of motor disconnect for a particular fixture. In that case, it may cause the motor to continue running even when disconnected from its power source, leading to mechanical failure or other hazards.
Importance Of Identifying And Understanding Different Types Of Disconnects
Electricians must be able to identify and understand the different types of disconnects such as NEMA and non-NEMA, fused vs. non-fused, enclosed vs.
NEMA And Non-NEMA Disconnects
NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) and Non-NEMA disconnects are two categories of disconnecting means used in electrical systems. These categories define the design and manufacturing standards of the electrical equipment, which directly impacts its reliability and performance. Understanding the differences between them is crucial for choosing the right type of disconnect for your electrical projects.
| Factors | NEMA Disconnects | Non-NEMA Disconnects |
|---|---|---|
| Standards and Ratings | Follow NEMA guidelines for design, performance, and safety. | Do not adhere to NEMA standards but may follow other standards such as IEC or UL. |
| Environment Suitability | Designed to meet various environmental requirements, such as exposure to dust, water, or corrosive substances. | May not be designed for specific environmental conditions, making them suitable for limited applications. |
| Enclosure Types | Available in different NEMA-rated enclosures like Type 1, 3R, 4, and 12, depending on specific application requirements. | Enclosure types may vary and may not have specific ratings for protection against environmental factors. |
| Quality and Reliability | High-quality materials and stringent testing ensure better reliability and durability. | May not offer the same level of quality and reliability due to varied manufacturing standards. |
| Compatibility | Compatible with NEMA-rated equipment, making it easy to integrate into existing systems. | Compatibility with other equipment may vary, which may require additional components or modifications. |
| Cost | Generally more expensive due to higher quality materials and adherence to NEMA standards. | Typically less expensive but could have higher long-term costs due to potential performance and compatibility issues. |
When considering a disconnect for your electrical project, it’s vital to weigh the benefits and drawbacks of both NEMA and Non-NEMA disconnects. Understanding their differences will help you make a more informed decision and ensure the safety and efficiency of your electrical systems.
Fused Vs Non-Fused Disconnects
When it comes to electrical disconnects, there are two main types: fused and non-fused. Fused disconnects incorporate a fuse that will automatically cut off the flow of electricity in the event of an overload or short circuit. The fuse provides added protection against electrical hazards and can prevent damage to equipment and machinery. On the other hand, non-fused disconnects do not have fuses, making them less costly than their fused counterparts.
It’s important for electricians to understand which type of disconnect is needed for specific applications based on safety considerations and industry standards. For example, motor circuits often require a fused disconnect due to the potential damage that could occur if a motor were to seize up during operation and cause an overload. By contrast, lighting fixtures may not necessarily require a fused disconnect since they typically draw less current than motors.
Ultimately, whether you need a fused or non-fused disconnect depends on the unique requirements of each application. It’s up to electricians and other professionals in the field to make informed decisions about what kind of equipment best meets their needs while ensuring proper safety measures are taken at all times.
Enclosed Vs Open Disconnects
When it comes to disconnects, one important factor to consider is whether they are enclosed or open. Enclosed disconnects provide added protection from accidental contact with live components and environmental factors such as dust and moisture. These types of disconnects are commonly used in outdoor environments or where there is a high risk of exposure to the elements.
On the other hand, open disconnects allow for easier access and visibility during maintenance or troubleshooting activities. They are often found indoors and used in situations where frequent access is required, such as with motor controls or large machinery.
It’s important to understand which type of disconnect is appropriate for each situation based on safety concerns, accessibility needs, and environmental factors. Proper installation and maintenance also play a crucial role in ensuring that these devices operate correctly when needed. As an electrician, being aware of the different options available will ultimately lead to better decision-making when it comes to selecting the right equipment for any given scenario.
Proper Installation And Maintenance
To ensure proper functionality and safety, it is crucial to follow the appropriate procedures for the installation and maintenance of electrical disconnecting means. Below are some key points to keep in mind:
- Always consult manufacturer instructions and adhere to local codes and regulations regarding installation.
- Ensure that all power sources are turned off before beginning installation or maintenance.
- Verify that the correct type of disconnect is being used for the specific application.
- Check for proper wiring and grounding to prevent electrical hazards.
- Regularly inspect disconnects for damage or wear and tear, such as corrosion or loose connections.
- Replace any damaged components immediately with equivalent parts from the original manufacturer.
- Test disconnect switches periodically to verify proper functioning.
By following these guidelines, electricians can help prevent safety issues, protect against liability concerns, and maintain optimal performance of electrical systems for their clients.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electricians need to be well-versed in the proper terminology and functioning of disconnecting means for electrical work. Switches and disconnects are often used interchangeably, causing confusion among professionals in the field.
It is important to understand the different types of disconnects, including NEMA and non-NEMA options, fused vs non-fused versions, as well as enclosed and open varieties.
Proper installation and maintenance can mitigate safety concerns and potential liability issues.
Key Takeaways
- Disconnecting means are essential components of any electrical system, allowing electricians to safely perform maintenance or repairs on equipment by cutting off the supply of electricity from a primary source.
- Different types of disconnects include fusible and non-fusible versions, motor disconnects, circuit breaker disconnects, GFCI disconnects, and service entrance disconnects. It is important for electricians to understand these different types to ensure proper installation and maintenance.
- Proper installation and maintenance of disconnecting means are crucial not only for safety reasons but also to avoid potential liability issues that could result in serious harm to individuals and property damage. Electricians must prioritize safety above all else when completing high-quality work for their clients.
FAQs:
1. What do electricians mean by “what disconnects”?
Electricians use the term “what disconnects” to refer to devices that are used to interrupt or shut off electrical currents for safety purposes. These can include switches, circuit breakers, and fuses.
2. When should I call an electrician if my circuit breaker keeps tripping?
If your circuit breaker is frequently tripping, it may indicate a larger electrical issue that requires professional attention. It is recommended to call an electrician as soon as possible to assess and repair any potential problems.
3. How can I know if my home’s wiring needs upgrading?
Old or faulty wiring in your home can be dangerous and increase the risk of electrical fires or electrocution. Signs that your wiring may need upgrading include flickering lights, frequent power outages or surges, sparking outlets, burning smells, or visible damage to wires or cables.
4. Can I handle basic electrical repairs on my own?
While some minor electrical repairs such as replacing light fixtures or installing dimmer switches can be done safely by DIY enthusiasts with proper training and tools, it is generally not advisable for non-professionals to attempt more complex repairs involving live circuits without proper training and experience due to the significant risks of injury or death involved in doing so.